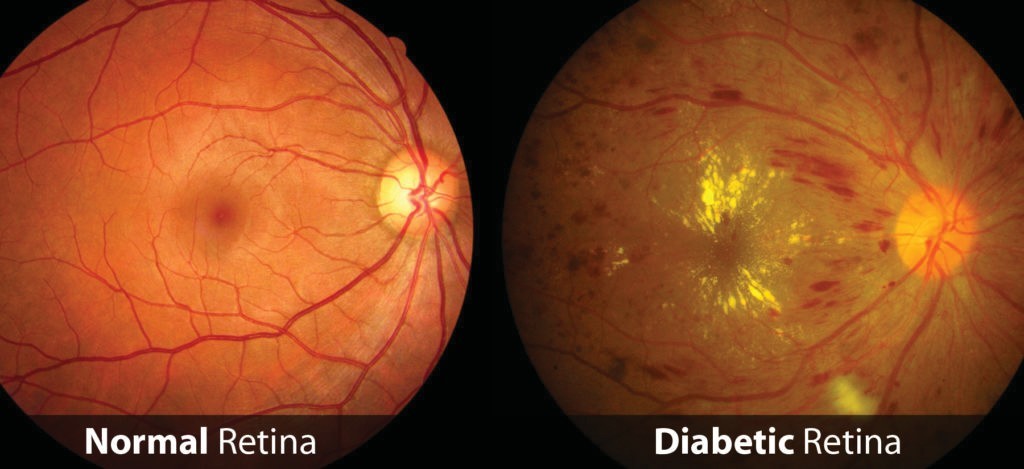
What is Diabetic Retinopathy?
Diabetic retinopathy is a diabetes complication that affects
the eyes. It is caused by damage to the blood vessels on a
light-sensitive layer (retina) at the back of your eye. When
blood sugar levels are high, these blood vessels can swell
and leak. They can also shut down, stopping blood from
passing through. Abnormal new blood vessels may grow on
the retina and possibly bleed into the cavity of the eye.
These changes can diminish your vision.
Stages of Diabetic Retinopathy
NPDR (Non-Proliferative Diabetic Retinopathy)
This is the early stage of diabetic eye disease. Many people
with diabetes have it. At this stage, your vision may or may
not be affected by the changes on the retina.
PDR (Proliferative Diabetic Retinopathy)
PDR is the more advanced stage of diabetic eye disease. It
happens when the retina starts growing abnormal and
fragile new blood vessels, that may often bleed into the jelly
eye substance (vitreous). They may give you floaters or
totally block your vision.
These new blood vessels can later form scar tissues. Scar
tissues can cause problems with the macula or lead to a
detached retina.
PDR is a serious condition, and can steal both your central
and peripheral (side) vision.
View Images
Who is at Risk?
People with all types of diabetes:
Risk of developing diabetic retinopathy can increase as a
result of:
-
Duration of diabetes — the longer you have
diabetes, the greater the risk of developing
diabetic retinopathy
-
Poor control of blood sugar level
-
High blood pressure
-
Pregnancy
-
High cholesterol
-
Tobacco use
Signs and Symptoms
-
Blurry vision
-
Dark spots
-
Floaters
-
Poor night vision
-
Vision that changes from blurry to clear
How Is Diabetic Retinopathy Diagnosed?
Your eye doctor will:
- Check your visual acuity
- Look for evidence of cataracts
- Measure your eye pressure
- Dilate your eyes
For this assessment, eyedrops are placed into your eyes
to widen your pupils to allow your doctor better view inside
your eyes. The drops may cause your near vision to blur
until they wear o", several hours later.
During the assessment, your eye doctor will look for:
- Abnormal blood vessels
- Swelling, blood or fatty deposits in the retina
- Growth of new blood vessels and scar tissue
- Bleeding in the clear, jelly-like substance that fills the center of the eye (vitreous)
- Retinal detachment
- Abnormalities in your optic nerve
Ancillary tests such as OCT (Optical Coherence Tomography) & FFA (Fundus Fluorescein Angiography) may be
done for finer details.
How to Prevent Diabetic Retinopathy
You cannot always prevent diabetic retinopathy. However,
regular eye exams, good control of your blood sugar
and blood pressure, and early intervention for vision
problems can help prevent severe vision loss.
If you have diabetes, reduce your risk of getting diabetic
retinopathy by doing the following:
- Manage your diabetes well
- Eating healthy
- Physical activity
- Ideal weight
- Take oral diabetes medications or insulin as directed
- Keep your blood pressure and cholesterol under control
- Quit smoking permanently
- Pay attention to vision changes - blurry/spotty/hazy
Remember, diabetes does not necessarily lead to blindness.
Taking an active role in diabetes management can help you save your vision and other diabetes-related
complications.
How to Treat Diabetic Eye Diseases
Treatment
Treatment, which depends largely on the type of diabetic
retinopathy you have and how severe it is, is aimed at
slowing or stopping progression of the condition.
Early diabetic retinopathy
If you have mild or moderate nonproliferative diabetic
retinopathy, you may not need treatment right away.
However, your eye doctor will closely monitor your eyes to
determine when you might need treatment.
Advanced diabetic retinopathy
If you have proliferative diabetic retinopathy or macular
edema, you will need prompt intervention. Depending on
the specific problems with your retina, options may include:
Photocoagulation:
-
Focal: This targeted laser treatment, can stop or slow
the leakage of blood and fluid in the eye. Focal laser
treatment is usually done in your doctor's eye clinic in a
single session.
-
Panretinal (PRP): This laser treatment, also known
as scatter laser treatment, can shrink the abnormal blood
vessels. During the procedure, the areas of the retina away
from the macula are treated with scattered laser burns. The
burns cause the abnormal new blood vessels to shrink and
scar.
It is usually done in your doctor's office or eye clinic in two
or more sessions. Your vision will be blurry for about a day
after the procedure. Some loss of peripheral vision or night
vision after the procedure is possible.
-
Vitrectomy: This procedure uses a tiny incision in
your eye to remove blood from the gel of the eye (vitreous) as
well as scar tissue that's tugging on the retina. It is done in a
surgery center or hospital using local or general anesthesia.
-
Injecting Medicine into the eye: Your doctor
may suggest injecting medication into the vitreous in the
eye. These medications, called vascular endothelial growth
factor (VEGF) inhibitors, may help stop growth of new blood
vessels by blocking the effects of growth signals the body
sends to generate new blood vessels.
Your doctor may recommend these medications, also called
anti-VEGF therapy, as a stand-alone treatment or in
combination with panretinal photocoagulation.
Surgery often slows or stops the progression of diabetic
retinopathy, but it is not a cure. Because diabetes is a
lifelong condition, future retinal damage and vision loss is
still possible.
Meet our specialist
Dr Ainur Rahman Dato Setia Dr Anuar Masduki
Designation
Consultant Ophthalmologist and Corneal Surgeon
Dr Chandra Kumar A/L Chandra Sekharan
Designation
Ophthalmologist
Dr Lee Ming Yueh
Designation
Consultant Ophthalmologist and Glaucoma Surgeon
Dato’ Dr Linda Teoh Oon Cheng
Designation
Consultant Ophthalmologist and Glaucoma Surgeon
Dr Nazila Ahmad Azli
Designation
Consultant Ophthalmologist and Oculoplastic, Lacrimal & Orbital Surgeon
Specialty
Ophthalmology,
Oculoplastic Surgery
Dr Norazah Abdul Rahman
Designation
Consultant Ophthalmologist, Paediatric Ophthalmologist and Strabismus Surgeon
Specialty
Ophthalmology,
Paediatrics Ophthalmology & Strabismus Surgery
Dr Ronald Arun Das
Designation
Consultant Ophthalmologist and Vitreo Retinal Surgeon
Datin Dr Teoh Su Lin
Designation
Consultant Ophthalmologist
Dr V. Ulagantheran Viswanathan
Designation
Consultant Ophthalmologist and Vitreo Retinal Surgeon